Page 5 - HIOKI 2017 Field Measuring Instruments
P. 5
5 About the catalog
Ensuring Safe Operation of the Product
To help you use measuring instruments safely, the following information is provided in each product's Instruction Manual under "Specifications":
• Rated voltage to ground: The measurement point's voltage level relative to ground, Measurement Category, Anticipated transient overvoltage, etc.
• Location for use: Pollution Degree 2, indoor, altitude no more than 2000 m, etc.
1 Measurement Category
Under safety standards (EN61010 Series, JIS C 1010 Series), measurement is classified into Categories II to IV according to the measurement point's rated voltage to ground,
current capacity (size of current that flows in a short-circuit fault), etc., and the transient overvoltage that occurs at the measurement point.
•Category II : Measurement at a point from the power plug to the equipment's power circuits, where equipment is directly connected to an outlet.
•Category III : Measurement at a point on the power distribution cabling or power supply circuits, or at a point from the distribution panel to a distribution
terminal behind an outlet, where equipment (for example a fixed installation) takes electricity directly from a distribution panel.
•Category IV : Measurement at a point on a service drop to a building, or on the line from the drop connection to the power meter or distribution panel.
The measurement instrument's Category is marked as "CAT II", CAT III"
or "CAT IV" near the measurement terminals.
Never measure a measurement point with a higher
category number than the category indicated on the
measuring instrument. Doing so could lead to a serious
accident such as electric shock.
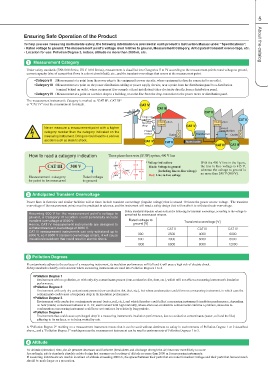
How to read a category indication Three-phase three-wire (3P3W) system, 400 V line
CAT III 300 V
* Voltage indications With the 400 V line in the figure,
Measurement category Rated voltage Black: Voltage to ground the line-to-line voltage is 415 V,
for point to be measured to ground (including line-to-line voltage) whereas the voltage to ground is
Red: Line-to-line voltage no more than 240 V (300 V).
2 Anticipated Transient Overvoltage
Power lines in factories and similar facilities will at times include transient overvoltage (impulse voltage) that is around 10 times the power source voltage. The transient
overvoltage of the measurement points must be predicted in advance, and the instrument will need a safety design that will enable it to withstand such overvoltage.
Assuming 600 V for the measurement point's voltage to Safety standards stipulate values such as the following for transient overvoltage, according to the voltage to
ground, a Category IV location could potentially include ground and the measurement category.
transient overvoltage of 8000 V.
Hence, CAT IV measurement instruments are designed to Rated voltage to Transient overvoltage [V]
withstand transient overvoltage of 8000 V. ground [V] CAT III
CAT III measurement instruments can only withstand up to
6000 V, so if 8000 V transient overvoltage enters, it will cause CAT II CAT IV
insulation breakdown that could result in electric shock.
300 2500 4000 6000
600 4000 6000 8000
1000 6000 8000 12000
3 Pollution Degrees
If contaminants adhere to the surfaces of a measuring instrument, its insulation performance will fall and it will pose a high risk of electric shock.
Safety standards classify environments where measuring instruments are used into Pollution Degrees 1 to 4.
•Pollution Degree 1
Environment with no pollution, or with only dry contaminants present (non-conductive dirt, dust, etc.), which will not affect a measuring instrument's insulation
performance.
•Pollution Degree 2
Environment with only dry contaminants present (non-conductive dirt, dust, etc.), but where condensation could form on a measuring instrument, in which case the
contaminants could cause a temporary drop in its insulation performance.
•Pollution Degree 3
Environment with conductive contaminants present (water, soil, etc.), and which therefore could affect a measuring instrument's insulation performance, depending
on how (much) contaminant adheres to it. Or, environment with high humidity, where even non-conductive contaminants could be a problem, since due to
condensation a measuring instrument could have wet surfaces for relatively long periods.
•Pollution Degree 4
Environment that could cause a prolonged drop in a measuring instrument's insulation performance, due to conductive contaminants (water, soil and the like)
adhering to its surfaces, or to being wetted by rain.
A "Pollution Degree 2" marking on a measurement instrument means that it can be used without detriment to safety in environments of Pollution Degree 1 or 2 described
above,, and a "Pollution Degree 3" marking means the measurement instrument can be used in environments of Pollution Degrees 1 to 3.
4 Altitude
As altitude (elevation) rises, the air pressure decreases and flashover (breakdown and discharge through the air) becomes more likely to occur.
Accordingly, safety standards stipulate safety design that assumes use locations of altitude no more than 2000 m for measuring instruments.
If measuring instruments are used in locations of altitude exceeding 2000 m, the spaces between their parts that are under hazardous voltage and their parts that humans touch
should be made larger as a precaution.